Evolving Core Web Vitals tactics using Cloudflare and WebpageTest
In our guide to Core Web Vitals tactics using Cloudflare and WebpageTest, we outlined basic requirements for using Cloudflare as a reverse proxy for testing tactical HTML changes with WebpageTest. Our version of the test is simplified from Patrick Meenan’s original concept, which uses HTMLRewriter() to select an element and modify code.
We’re going in-depth with this tutorial, but if you’re just looking for the Cloudflare Worker script, you can find it here.
Our first installment noted that it won’t keep up with changes at Search Engine Land. The LCP was hard-coded and we would need it to interact with a dynamic page and its values. While WebpageTest has, at the time of publication, the most well-thought-out waterfall chart and more details than you can imagine, it isn’t the fastest way to get results.
Lighthouse from the Command Line
Running the Lighthouse CLI (Command Line Interpreter) program with --extra-headers options needed for the test allows us to also simulate standard settings for Core Web Vitals the way we did with WebpageTest. You’ll need to work from a terminal emulator.
The easiest way to install Lighthouse is with NPM (Node Package Manager). Once installed, run the following statement:
$ lighthouse https://sel.deckart.workers.dev --extra-headers "{"x-host":"searchengineland.com", "x-bypass-transform":"false"}" --form-factor=mobile --throttling.cpuSlowdownMultiplier=4 --only-categories=performance --view
The evolution of our Testbed
Our aim is to demonstrate an evolution from an original concept for a testbed to a project suitable for our future events and articles. The testbed should not be confined to running performance evaluations; that’s just where we’ll start. But, it has to work fairly well for a number of situations with websites and this can prove pretty difficult. We’ll supply methods to help.
For example, sites often use relative paths to asset resources rather than absolute (with HTTP protocol and all). We’ll supply a block to match these so HTML will generally work. After applying this, when things still don’t work, switching troublesome references between the test and test subject hostnames often does the trick, even for CORS policy violations.
That’s where the beauty of Cloudflare’s HTMLRewriter() really shines. Site-wide assets are usually loaded as page HEAD child elements. With flexibility matching like jQuery, even similar syntax, we can select child elements of HEAD when necessary. You can use XPath selectors and regular expressions. Let’s keep it simple and look for relative paths that start with “/” for src or href attributes:
return new HTMLRewriter()
.on('link', {
element: el => {
link_href = el.getAttribute('href');
if (link_href && link_href.startsWith('/')) {
el.setAttribute('href', 'https://' + host + link_href);
}
}
})
.on('script', {
element: el => {
script_src = el.getAttribute('src');
if (script_src && script_src.startsWith('/')) {
el.setAttribute('src', 'https://' + host + script_src);
}
}
})
.on('img', {
element: el => {
img_src = el.getAttribute('src');
if (img_src && img_src.startsWith('/')) {
el.setAttribute('src', 'https://' + host + img_src);
}
}
})We’re leveraging the power (and cost effectiveness) of Edge Computing to conduct seriously useful tests. Modify the x-host request header to load different sites in the testbed and open DevTools. Transformations may not be needed, but your mileage will vary. Frontend experience gives you a feel for it.
Comment blocks like switches will fail and require a little experimentation (which may be all you need). For example, some asset references may be spelled without HTTP colon. You would need to write another conditional to check for paths where href or src starts with “//” and then modify the selected element value in the script. Try to end up with no console errors the actual site doesn’t have.
Lighthouse gives you LCP
It’s relatively easy to retrieve LCP references using Lighthouse, PageSpeed Insights or WebpageTest. Presuming the LCP qualifies for preload, like when it’s not a <div> or a <p>, and when it isn’t already getting preloaded, provide our script the href value by URL ‘query param’ structure (or return HTML with a form) to test for changes to a page’s LCP timing with preload.
Most technical SEO practitioners are handy at modifying request query parameters to process different things in server-side programs, like Google search results. Using the same interface, our script will preload the LCP using the path you apply in the “lcp” parameter value and passes it to a function called addPreloadAfter() for interpolating HTML for the test.
async function handleRequest(request) {
const { searchParams } = new URL(request.url);
let lcpHref = searchParams.get("lcp");
return new HTMLRewriter()
.on('title', addPreloadAfter(lcpHref))
.transform(newResponse);
}The addPreloadAfter() function takes our “lcpHref” value from searchParams.get() and processes it as “href” to build HTML.
const addPreloadAfter = (href) => ({
element: (el) => {
el.after(`<link rel="preload" href="${href}" />`, { html: true });
}
});Notice the option “html: true”? This is an option setting Cloudflare requires for safety when using Workers with HTMLRewriter() API methods that write HTML. You are going to want to learn its capabilities and constraints for coding your own tests.
Cloudflare’s KV
If we’re ever going to do anything remotely interesting, we need a way to store persistent data between script executions. Luckily, Cloudflare also offers a neat little data storage mechanism called KV that we can bind with our Workers to store a small data ‘value‘ field, accessible by its ‘key.’ It’s surprisingly easy to comprehend and implement. To demonstrate how to use it we’ll write a quick little hit counter.
const counter = await KV.get("counter");
if (!host || counter > 1000) {
return new Response('hit limit exceeded or x-host missing', {status: 403});
} else {
await KV.put("counter", parseInt(counter) + 1);
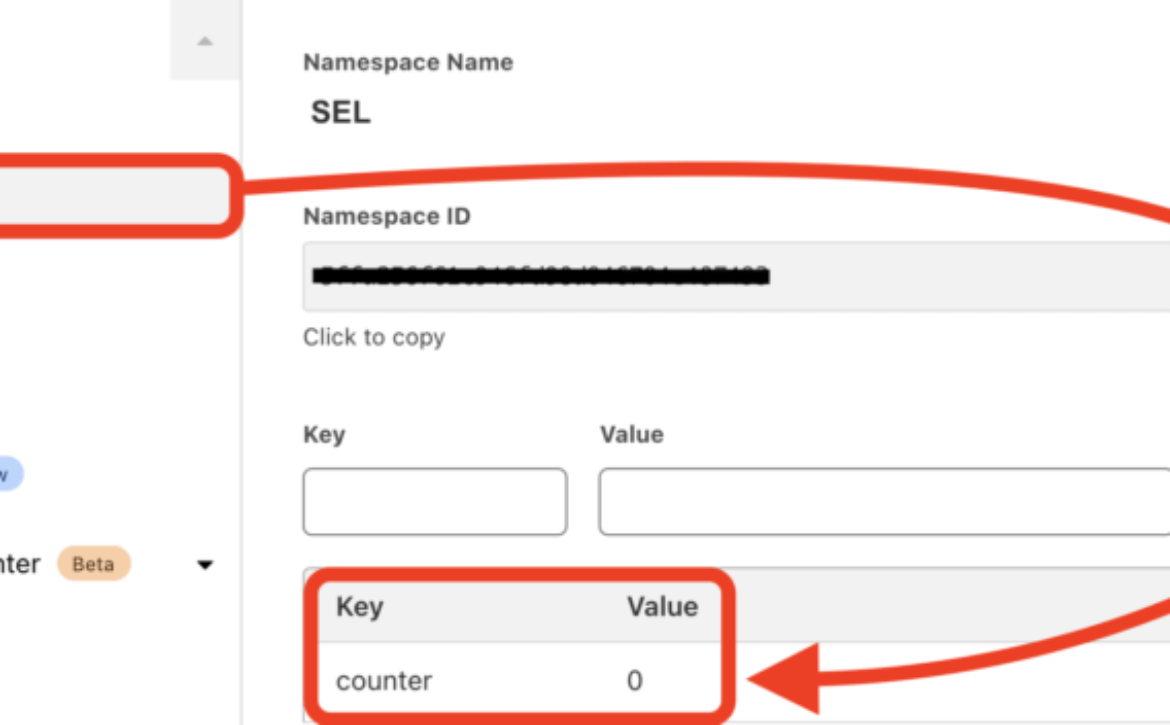
}Find the KV navigation menu item under Workers.
Once you’ve created a Namespace (“SEL” is used in the example above), use the KV dashboard UI to create your first Key (‘counter‘ in the above case) and assign a starting value. Once set up, navigate back to the Worker dashboard for the interface required to bind our new KV Namespace with Cloudflare Workers so they can access Keys and the associated stored Values.
Bind KV Namespaces to Workers
Choose the Worker you want to bind with and click its Settings menu to find the submenu for Variables (directly under General). Notice you can define environment variables, Durable Object Bindings (which we’ll explore in a future installment), and finally KV Namespace Bindings. Click Edit Variables and add the Variable you want to use in script.
In the following case, you can see our redundantly named ‘KV‘ variable that we’ll be using in the associated Worker script, the one we navigated from. Our use of ‘KV‘ was named for illustrative purposes. Select it from the dropdown, save it, and you’ll immediately be able to use your variable in the script. Create as many scripts and KV Namespaces combinations as you like.
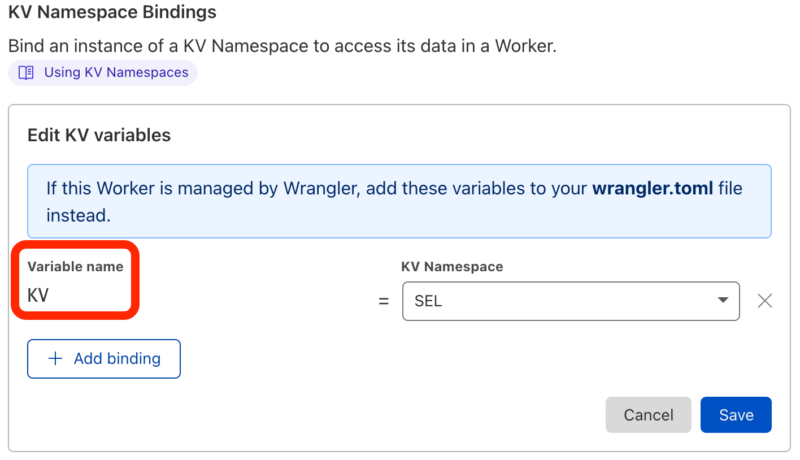
The trick is remembering to bind a Variable you want used in the Worker. It’s so flexible that you can feel free to munge about and make a mess at first. You’ll probably be able to organize it into something cohesive at a later date, which is exactly what you want for being able to prototype applications or author Microservices for use in your applications.
Once you’ve gotten your KV service and starting values set up, navigate back to the Worker and open the built-in “Quick Edit.” Replace what’s there with this updated gist, which includes the hit counter, and everything else written about in this post. Click “Save and Deploy” and you should have the service up and running at your publicly available, Workers demo URL.
Why we care
Our original guide was meant to whet your appetite, get you excited to start and excited for more valuable learning. In order to supply that, we have a free platform and code combination that is simple enough to understand on its own, coupled with a process that should be easy enough to follow and achieve a test result.
Standardizing website testing to demonstrate SEO to developers shouldn’t require understanding code when you can copy and paste script into Cloudflare, follow steps and test certain SEO tactics. Core Web Vitals tests are about as reliable as we’re going to get for improving RUM (Real User Metrics) performance scores for a boost in rankings, given how metrics dependent it is.
The post Evolving Core Web Vitals tactics using Cloudflare and WebpageTest appeared first on Search Engine Land.




 John
John