Google unveils multimodal search, new SERP features; Thursday’s daily brief
Search Engine Land’s daily brief features daily insights, news, tips, and essential bits of wisdom for today’s search marketer. If you would like to read this before the rest of the internet does, sign up here to get it delivered to your inbox daily.
Good morning, Marketers, Google’s Search On event was yesterday and we’ve covered all the announcements below.
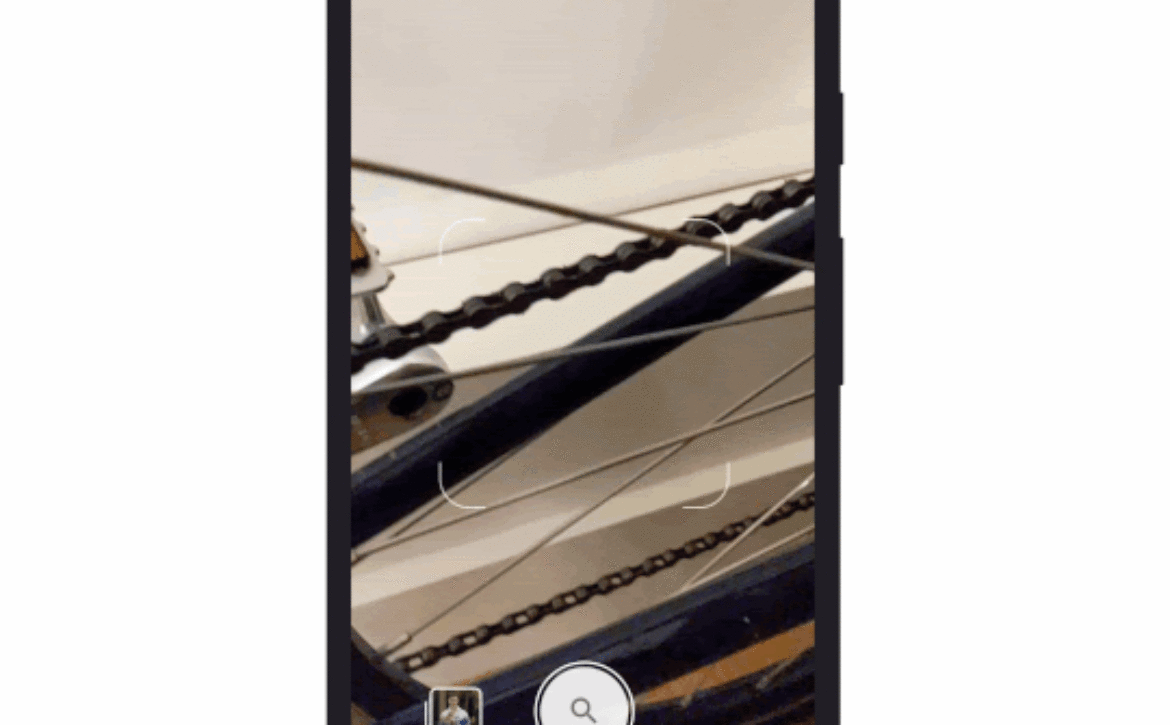
The leading announcement was MUM’s integration with Lens to produce the first instance of multimodal search available to the public (launching in English in the coming months). Although it’s not a complete departure from what we’re used to, being able to snap a photo and add some text is definitely a new way to search.
At the event, Google provided an e-commerce use case for it (more on that below). I’m interested in learning more ways you think these capabilities might benefit businesses. Send me an email at gnguyen@thirddoormedia.com (subject line: A picture and a thousand words), and don’t hold back, these capabilities were unheard of a decade ago, yet here we are.
That’s just one of the many announcements from Search On, keep on scrolling to get caught up on newly announced SERP features, enhancements and more.
George Nguyen,
Editor
MUM brings multimodal search to Lens, deeper understanding of videos and new SERP features
Google announced new applications of its MUM technology, including multimodal search with Google Lens, Related topics in videos and other new search result features, at its Search On event on Wednesday. While these announcements are not an overhaul of how Google Search works, they do provide users with new ways to search and give SEOs new visibility opportunities as well as SERP and search changes to adapt to.
- MUM enhancements to Google Lens (shown above): Google demoed a new way to search that combines MUM technology with Google Lens, enabling users to take a photo and add a query. E-commerce is another potential use case — users can take a picture of a pattern on a shirt and ask Google to find the same pattern on socks, the company provided as an example.
- Related topics in videos: Google is also applying MUM to show related topics that aren’t explicitly mentioned in a video. This will be launching in English in the coming weeks, and the company will add more visual enhancements over the coming months. It will first be available for YouTube videos, but Google is also exploring ways to make this feature available for other videos.
- “Things to know”: This SERP feature lists various aspects of the topic the user searched for — for example, if the query were “acrylic painting,” the searcher might see a step-by-step guide or tips in this section. This feature can enable users to see the different dimensions other people typically search for, which may help them get to the information they’re looking for faster.
- Refine and broaden searches: This set of features act like search suggestions in the SERP, enable users to get more specific with a topic or zoom out to more general topics.
Google search gets larger images, enhances ‘About this result,’ gets more ‘shoppable’ and more

While MUM was the highlight of Google’s Search On event, the company also announced a number of changes to the search results that are important for search marketers to understand. These changes include:
- More visually browsable search results. For queries in which users may want to explore information visually, like “painting ideas,” Google may show a more image-heavy results page. This type of results page may also display for apparel-related queries.
- “About this result” enhancements. Initially launched in February and expanded to include ranking information in July, this transparency feature now includes what the site in question says about themselves (which can be pulled from places like the “About Us” page) and can also show web results about the site, such as what others are saying about it, or related results about the topic.
- Shoppable search. Now, when users browse for apparel on mobile, Google may show a visual feed of related items in various colors and styles, along with other information like style guides, videos or local shops. This feature is powered by the Google Shopping Graph and is currently limited to the U.S.
- Local in-stock filters. Beginning today in English in the U.S., UK, Australia, Austria, Brazil, Canada, Denmark, France, Germany, Japan, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Sweden and Switzerland, users may see an “in stock” filter that allows them to see if nearby stores have a specific item available on their shelves.
- Shopping with Google Lens. Soon, Google app users on iOS will see a new button that makes all the images on a page searchable via Google Lens. Similar functionality will also be arriving on Chrome for desktop: Users will be able to select images, video or text on a site to see search results in the same tab. Unlike the iOS version of this feature, which is only available in the U.S., Lens in Chrome will be available globally in the coming months.
Why we care. Review these new changes Google has rolled out and will be rolling out. See how you and your clients can leverage some of these changes to generate more business and traffic. The one area of concern is the About this result section having third-party information outside of Wikipedia that may be hard to change if it doesn’t have the most positive or accurate information about your company.
Another record-breaking holiday shopping season? Perhaps not…
Why container shipping delays are a big deal for e-commerce PPC in 2021. “The holidays this year are going to be even more different than last year,” said Fred Vallaeys, CEO at Optmyzr, “The effects of much higher shipping costs are going to be significant and ripple throughout the retail ecosystem.” In his post, Vallaeys breaks down how increased shipping costs will impact what retailers stock, the structure of their PPC campaigns and how customers may adapt.
You wrote an amazing article — here’s why influential people aren’t sharing it. This Twitter thread from SparkToro contains some pointers on why you’re not getting amplified and how you can go about changing that.
Not by design, but still racist. Under the “Safety” section of a People also ask box, Google showed “What percent of Fort Collins is Black?” Google Search Liaison Danny Sullivan explained how this unfortunate coincidence might’ve occurred. I’m not sure if this was a factor, but biased language models can result from internet training data, and it’s on every SEO and user to submit feedback so that the internet can be a place that’s safe for everybody.
What We’re Reading: The case for zero-party data
“When your data request is communicated transparently, 0P data helps build more trusted customer relationships that lead to higher lifetime value and 0P data, unlike some other methods, is free,” wrote John Cosley, senior director, brand marketing at Microsoft Advertising, “Plus, it’s more likely to be compliant and accurate, so incorporating it into your overall data strategy can better protect you as industry regulation evolves.”
With the looming demise of third-party cookies, there’s been an increased emphasis on first-party data, but, as Cosley reminds us, data that customers willingly provide you (zero-party data, or 0P data), is “the digital version of walking into a business and being immediately greeted by staff who ask how they can help you. It’s the main difference of how 0P data delivers a better value exchange over other consented models. The consumer now has skin in the game that forms a connection and directs the conversation.”
Brands can and should use zero-party as part of their larger strategy, which could also include first- and second-party data. One of the points Cosley emphasized was that brands should be mindful of how they’re asking for it: “You’ll find some opportunities immediately and others that will take more time to nurture. It could be off-putting for a person’s first experience with your brand to come with too many potentially personal questions, so gauge your approach accordingly,” he said.
He also shared the following tactics on obtaining your own zero-party data and using it in your advertising:
- Set up Universal Event Tracking (UET) to collect data to measure and tune your ad campaigns.
- Leverage tools like Custom Audiences to deliver personalized messages and offers with UET data.
- Use remarketing to reengage customers and prospects.
- Create look-alike, or Similar Audiences, lists and segments based on signals obtained through the above to provide more personalized ad experiences at greater scale.
The post Google unveils multimodal search, new SERP features; Thursday’s daily brief appeared first on Search Engine Land.